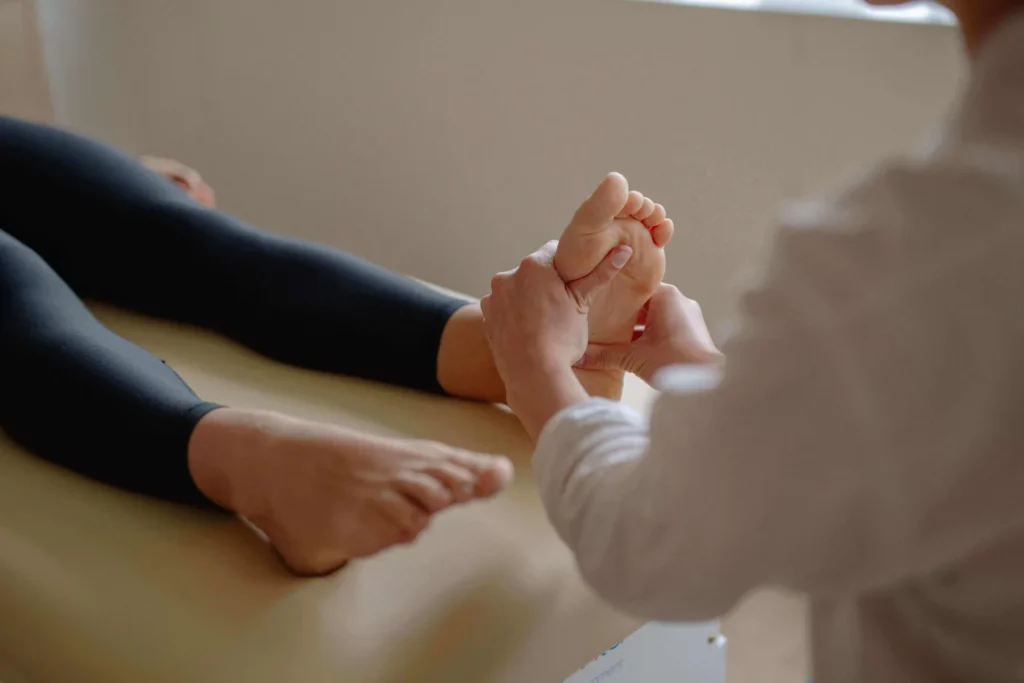
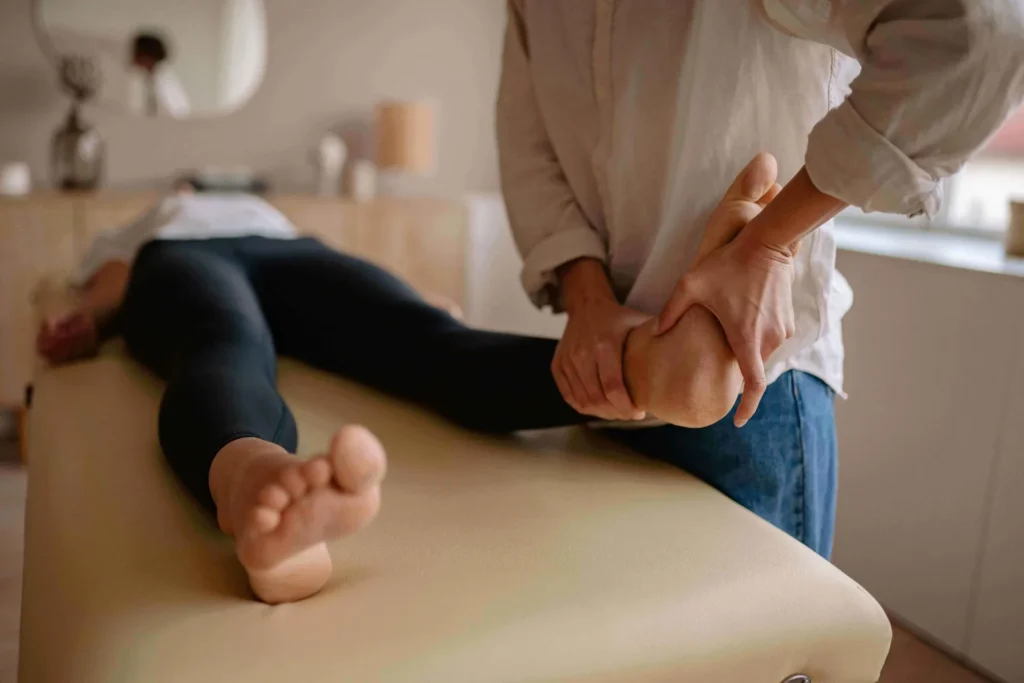
Heel Pain is a common complaint among patients seeking podiatric care. As a podiatrist, understanding the various causes and treatment options for heel pain is crucial in providing the possible care. This in-depth article will explore the potential causes, symptoms, and treatment options for heel pain to help you better serve your patients.
Common Causes of Heel Pain
It can result from various conditions, each with its own underlying cause. Some of the most common causes include:
- Plantar fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes, can lead to heel pain.
- Achilles tendinitis: Inflammation and degeneration of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone, can cause pain in the back of the heel.
- Heel spur: A bony growth on the underside of the heel bone can cause pain and inflammation, often associated with plantar fasciitis.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac that cushions the heel, can result in pain and swelling.
- Stress fractures: Tiny cracks in the heel bone, often caused by repetitive stress or force, can lead to heel pain.
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome: Compression of the tibial nerve as it passes through the tarsal tunnel can cause heel pain and other symptoms.
Symptoms Associated with Heel Pain
The specific symptoms of heel pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, some general symptoms may include:
- Pain in the bottom or back of the heel
- Swelling or redness around the affected area
- Stiffness or limited range of motion in the foot or ankle
- Tenderness when pressing on the heel
- Pain that worsens with activity or after prolonged standing
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Heel Pain
As a podiatrist, accurately diagnosing the cause of it is essential to develop an effective treatment plan. The diagnostic process may involve a physical examination, medical history, and imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound.
Once a diagnosis has been made, a variety of treatment options may be considered, including:
- Rest and activity modification: Limiting activities that aggravate heel pain and allowing time for the affected structures to heal is crucial.
- Ice and elevation: Applying ice and elevating the foot can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Footwear modifications: Wearing supportive shoes with proper cushioning and arch support can help minimize it.
- Orthotics: Custom orthotics can redistribute pressure on the foot, provide additional support, and alleviate pain.
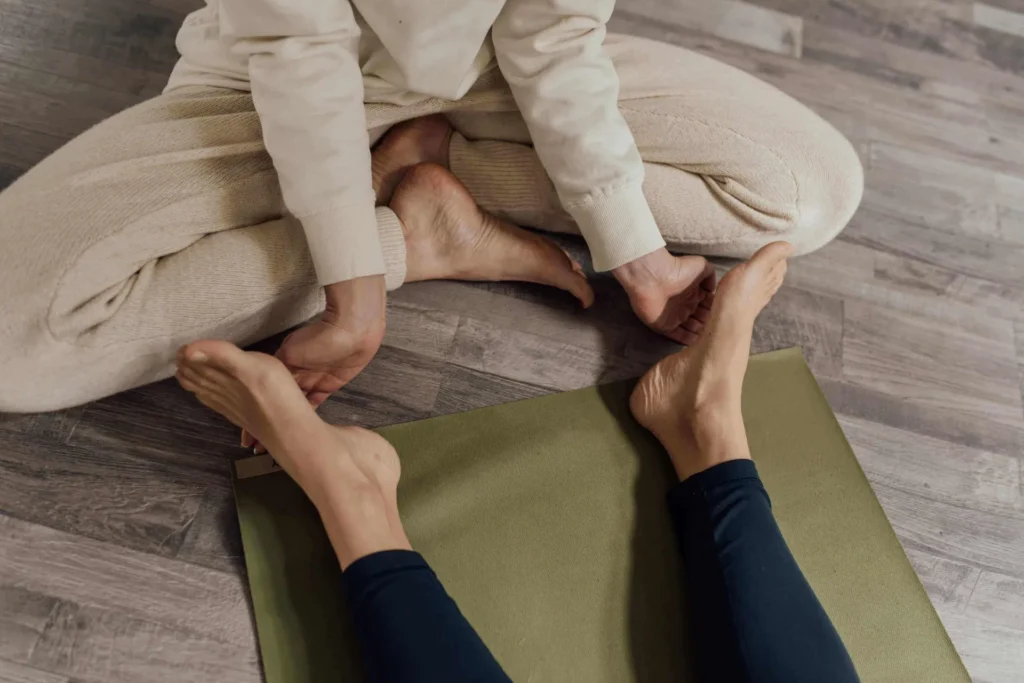

- Stretching and strengthening exercises: A podiatrist or physical therapist can recommend exercises to improve flexibility, strengthen muscles in the foot and ankle, and promote healing.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Over-the-counter or prescription anti-inflammatory medications can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid injections: In some cases, a corticosteroid injection may be recommended to provide temporary pain relief and reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: In rare cases, when conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered.
Conclusion
It is a common and often debilitating condition that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. As a podiatrist, understanding the various causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential in providing comprehensive care. If you or someone you know is experiencing it, consult a podiatrist to receive a thorough evaluation and tailored treatment plan to address the specific needs of each patient.


